Introduction:
Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE) is a minimally invasive procedure designed to treat certain gynecological conditions, particularly those related to the uterus. This document provides essential information about the procedure, its purpose, risks, benefits, and what to expect before, during, and after the intervention.
Procedure Overview:
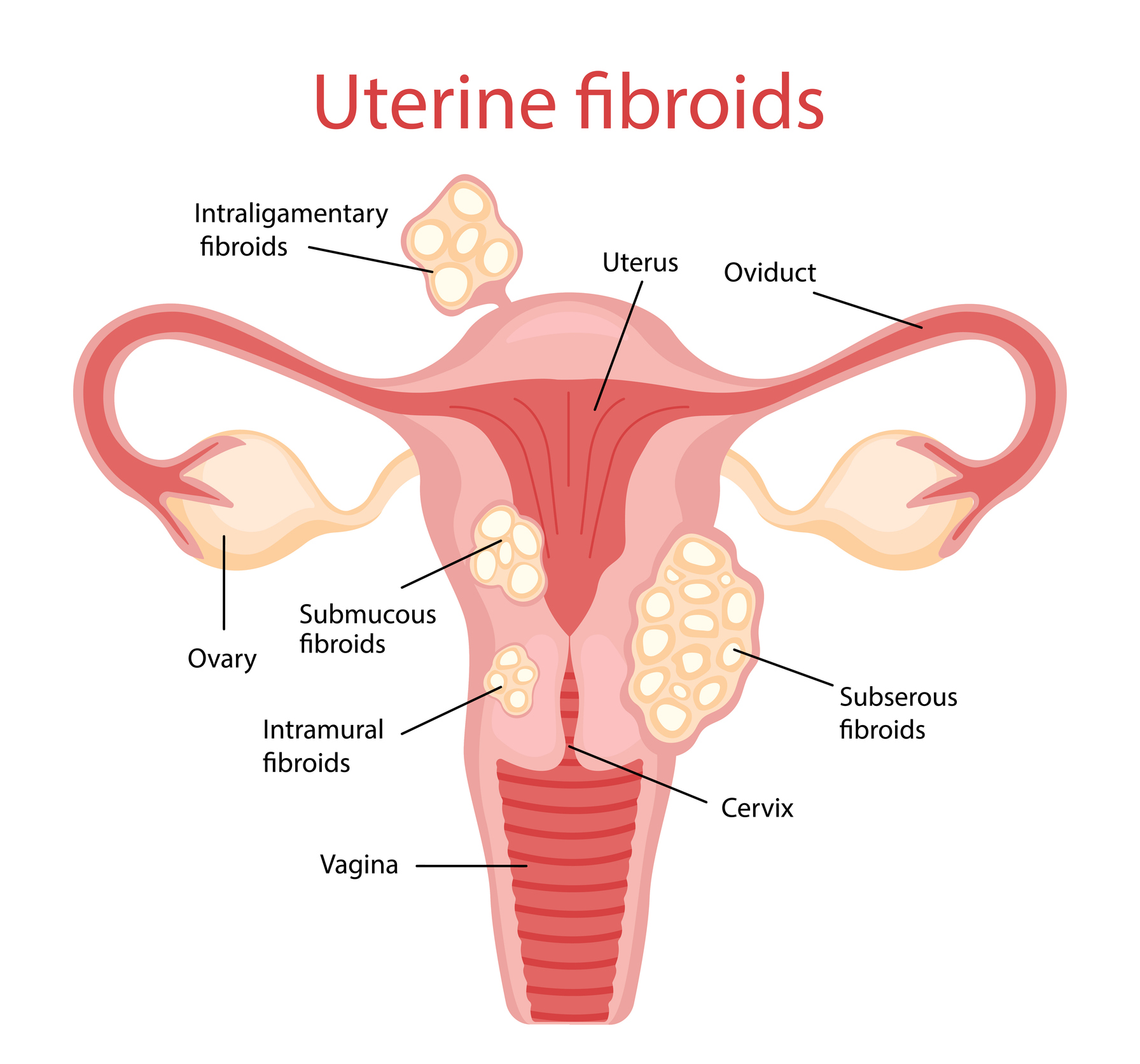
Uterine Fibroid Embolization involves the injection of small particles into the uterine arteries to block blood flow, leading to the shrinkage of uterine fibroids or the reduction of blood supply to abnormal tissue in the uterus. This procedure is commonly used to alleviate symptoms such as heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, and pressure.
Purpose of the Procedure:
UFE is performed to address various gynecological conditions, including uterine fibroids, adenomyosis, and other vascular abnormalities in the uterus. The goal is to reduce symptoms and improve the patient's quality of life without resorting to more invasive surgical options.
Risks and Benefits:
Benefits:
- Minimally invasive with a shorter recovery time compared to traditional surgery.
- Preservation of the uterus, making it a fertility-sparing option.
- Effective in reducing symptoms such as heavy bleeding, pelvic pain, and pressure.
Risks:
- Infection: There is a small risk of infection, typically treated with antibiotics.
- Embolization of unintended vessels: Rarely, particles may travel to unintended areas, potentially causing complications.
- Post-embolization syndrome: Temporary symptoms like pain, nausea, and fever may occur but can be managed with medication.
- Impaired fertility: While fertility is usually preserved, there is a small risk of early menopause in some cases.
Preparation:
Before the procedure, your healthcare team will provide specific instructions, which may include fasting, medication adjustments, and cessation of blood-thinning medications. It is crucial to inform your healthcare provider of any allergies, existing medical conditions, or medications you are currently taking.
During the Procedure:
UFE is typically performed by an interventional radiologist. You will be given a mild sedative to help you relax. A small incision is made in the groin area, and a catheter is threaded through the blood vessels to the uterine arteries. Contrast dye is injected to visualize the arteries, and then embolic particles are introduced to block blood flow to the targeted areas.
After the Procedure:
Following UFE, you may experience some discomfort, but this can be managed with pain medications. Most patients can resume normal activities within a week, although recovery times may vary. Close follow-up with your healthcare provider is essential to monitor your progress.
Conclusion:
Uterine Fibroid Embolization is a valuable option for managing certain gynecological conditions, offering a balance between effectiveness and minimally invasive intervention. Your healthcare team will provide personalized guidance based on your specific medical history and needs. Please feel free to ask any questions or seek clarification regarding the procedure.
Advanced Urology Institute